Author: Dr.Asha Anne Jacob ( Specialist Ophthalmologist – WELLKINS Medical Centre)
In our current pandemic-driven reality, where everything from education and job interviews to conferences and entertainment has shifted online, it’s undeniable that instances of digital eye strain have significantly multiplied. This condition, also known as Computer Vision Syndrome (CVS), encompasses a range of eye and vision-related discomforts resulting from prolonged engagement with digital screens such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and e-readers.
The age spectrum is no barrier to this predicament; it affects people of all ages. The severity is intricately tied to the duration of screen exposure. Extended periods of screen fixation invariably lead to sensations of eye fatigue, dryness, aching around and behind the eyes, and even headaches by the end of the day. Visual blurring may also occur as a consequence.
Essentially, we’re all denizens of the digital realm (you wouldn’t be reading this text otherwise!), and the pandemic has merely accelerated our reliance on digital devices.
Recognizing that experiencing digital-related eye strain or Computer Vision Syndrome is nearly inevitable, it’s prudent to consider a few strategies for alleviating the associated discomfort:
Practice Conscious Blinking:
The ocular surface relies on consistent moisture provided through blinking. However, prolonged screen exposure reduces the frequency of blinking, leading to dryness. Air-conditioned environments exacerbate this drying effect. Hence, make a deliberate effort to blink frequently to maintain adequate eye moisture.

Adopt the ’20-20-20′ Rule:
During prolonged periods of digital screen usage, remember the “20-20-20” guideline. Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to gaze at an object positioned 20 feet away. This simple practice eases the strain on your eye muscles.
Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second pause to focus on an object located at least 20 feet away. This simple habit helps relax your eye muscles and reduces the strain caused by continuous screen exposure.
 Optimal Seating and Screen Positioning:
Optimal Seating and Screen Positioning:
When you find yourself in front of a computer screen, it’s crucial to pay attention to your seating arrangement and screen positioning to promote optimal eye comfort. To start, ensure that you are seated at a suitable distance from the screen, which is generally around the length of your arm, approximately 25 inches away. This distance strikes a balance between being too close, which can lead to undue strain, and being too far, which may cause you to squint and strain your eyes to see the content clearly.
Equally important is the angle at which you position the screen. To alleviate strain on your eyes, try positioning the screen slightly below your direct line of sight. This means that your gaze should be directed slightly downwards when you’re viewing the screen. This slight tilt can make a significant difference in reducing eye strain, as it minimizes the amount of effort your eye muscles need to exert to maintain focus.
Avoiding a straight-ahead or upward gaze is essential for multiple reasons. When your screen is directly at eye level, it can cause you to open your eyes wider, leading to dryness and fatigue. On the other hand, looking upward can create additional strain on your neck and shoulder muscles. By angling the screen downward, you’re helping your eyes stay more relaxed and aligned with their natural resting position.
Remember that the goal here is to create a setup that promotes a comfortable and natural posture for your eyes. This means that your eyes should be able to move effortlessly across the screen without needing to constantly adjust their focus. By following these tips and positioning your screen thoughtfully, you can significantly reduce the strain on your eyes during prolonged computer usage, ensuring a more enjoyable and healthier screen-heavy experience.
Mitigate Glare:
Arrange your computer setup in a location with minimal direct sunlight. Eliminate overhead lights that cast glare on your screen. Employ an ‘Anti-glare filter’ to minimize screen glare. Adjust your screen’s brightness to match your ambient lighting conditions and consider enhancing screen contrast.
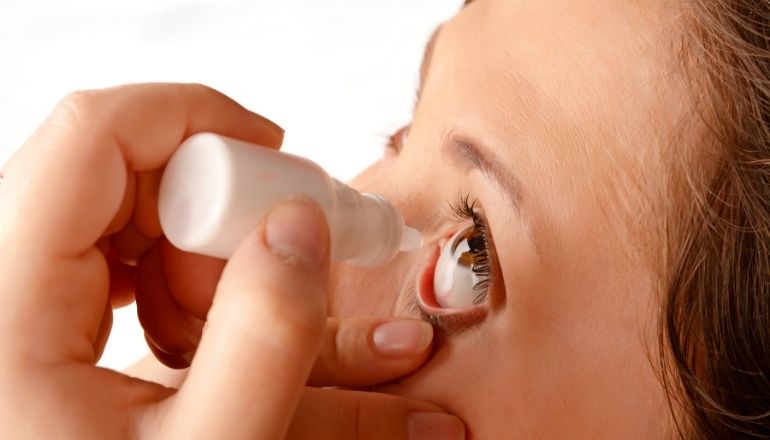

Use Lubricating Eye Drops:
Seek advice from an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) for suitable lubricating eye drops to apply when your eyes feel dry and strained.
Regular Eye Examinations:
Uncorrected or under-corrected refractive errors can exacerbate digital eye strain. Periodic visits to an ophthalmologist will help address any refractive issues and provide appropriate corrective measures.
In navigating our digital existence, these practical tips can significantly mitigate the discomfort associated with prolonged screen usage. By conscientiously attending to our eye health, we can better appreciate the benefits of our digital interconnectedness while minimizing its potential drawbacks.
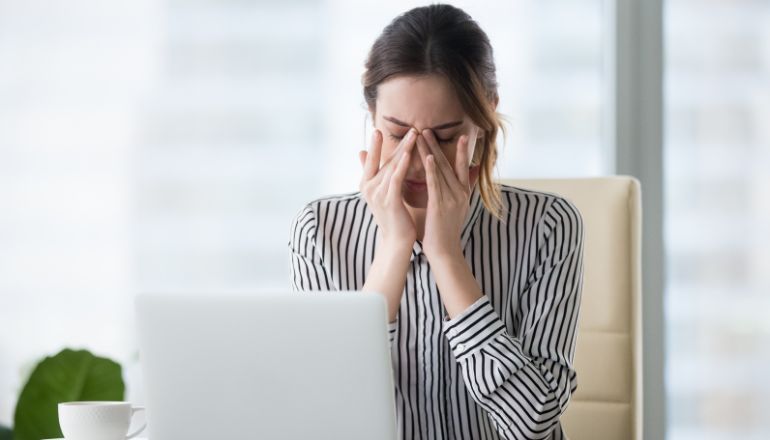



 Optimal Seating and Screen Positioning:
Optimal Seating and Screen Positioning: