Author: Dr.Reneesh (Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon – WELLKINS Medical Centre)
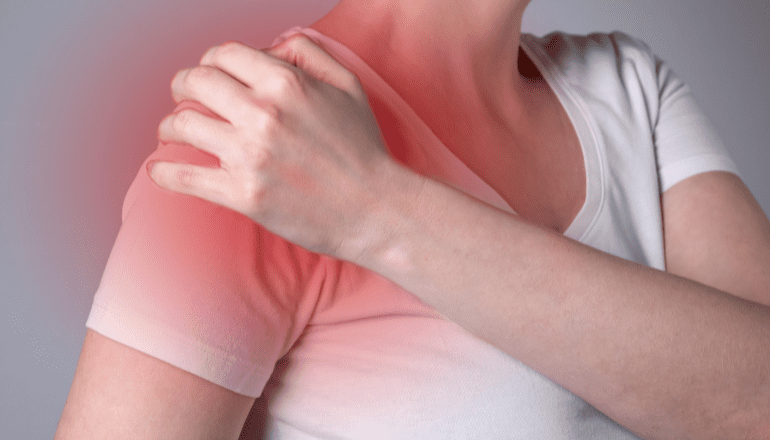
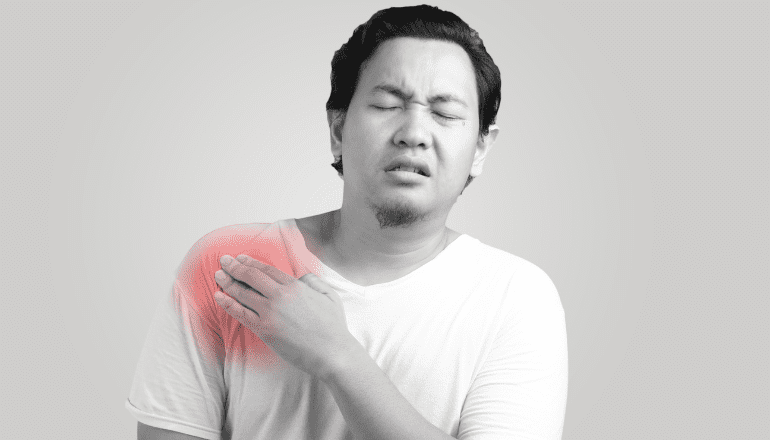
Shoulder pain is a common ailment that can result from various factors, encompassing injuries, overuse, and arthritis. The shoulder is a complex joint with a wide range of motion, making it susceptible to diverse issues. Injuries, such as rotator cuff tears, dislocations, and fractures, can lead to acute pain. Overuse, often seen in athletes or individuals with repetitive shoulder movements, can cause strain and inflammation.
Shoulder pain is a common ailment that can affect people of all ages. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, overuse, and arthritis. In some cases, shoulder pain may be a symptom of a more serious medical condition.
Common causes of Shoulder Pain
Rotator cuff injuries:
Rotator cuff injuries, the primary cause of shoulder pain, result from a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Overuse, sudden trauma, or degenerative changes can trigger these injuries. Overuse, often seen in repetitive activities like painting or weightlifting, leads to gradual wear, causing inflammation and tears in the tendons (tendinitis). Trauma, such as falls or direct blows, can result in immediate, severe tears. Aging contributes to degeneration, making the tendons more susceptible to damage.
Symptoms include pain, weakness, and restricted shoulder movement. Early recognition and intervention are crucial for preventing chronic shoulder pain and ensuring optimal function.
Bursitis:
Bursitis, the inflammation of fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints, is often triggered by overuse or injury. Repetitive motions or excessive pressure on joints can lead to irritation, causing pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. In some cases, direct trauma or infection may be the cause. Symptoms include localized pain, tenderness, and swelling around the affected joint.
Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms is crucial. Infectious bursitis necessitates antibiotic treatment. Preventive measures include taking breaks during repetitive tasks, maintaining proper form, and using protective equipment. Early recognition and appropriate management are essential for alleviating symptoms and restoring joint function.
Arthritis:
Arthritis, characterized by joint inflammation, encompasses various types, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common ones affecting the shoulder. Osteoarthritis results from the gradual wear and tear of joint cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, causes the immune system to attack the joints, resulting in inflammation and potential joint damage. Both conditions significantly impact shoulder function and require tailored treatment approaches.
Frozen Shoulder:
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, restricts shoulder movement due to thickening and tightening of the joint capsule. While its exact cause is unclear, factors like age and certain health conditions may contribute. The condition progresses through stages, causing pain and stiffness over months to years.
Tendinitis:
Shoulder tendinitis, inflammation of tendons connecting muscles to bones, stems from overuse, sudden trauma, or degenerative changes. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and tenderness. Management involves rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications, with physical therapy for muscle strengthening. Preventive measures include proper warm-up and maintaining good posture. Early recognition and intervention are key to effective treatment and preventing chronic tendinitis.
Impingement syndrome:
Impingement syndrome arises when the tendons of the rotator cuff get pinched between the bones of the shoulder joint, leading to pain, inflammation, and weakness in the shoulder. The condition is often associated with repetitive overhead movements or structural abnormalities in the shoulder. Management includes rest, anti-inflammatory measures, and physical therapy to alleviate symptoms and prevent further impingement. Early intervention is crucial for effective treatment and to avoid long-term complications.
Other causes of shoulder pain can include:
Bone spurs Broken bones, Dislocated shoulder, Separated shoulder, Thoracic outlet syndrome, Referred pain from other organs.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Pain:
Treatment for shoulder pain will vary depending on the underlying cause, but may include rest, ice, physical therapy, medications, or surgery.
Prevention Tips for Shoulder Pain
Warm-Up Before Exercising:
Ensure you properly warm up before engaging in physical activities to prevent strain on the neck and shoulder muscles.
Avoid Overuse:
Be mindful of repetitive motions that can lead to overuse and contribute to shoulder and neck pain.
Strengthen Shoulder Muscles:
Incorporate exercises that strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint, promoting better support and reducing the risk of pain.
Maintain Good Posture:
Proper posture is essential in preventing neck pain. Be conscious of your sitting and standing positions.
Lift Heavy Objects with Proper Form:
When lifting heavy objects, ensure you use proper form to avoid strain on your shoulders and neck.