Author: Dr.Reneesh (Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon – WELLKINS Medical Centre)
As an orthopedic surgeon, I frequently encounter patients with sprains and strains. While these injuries are common, improper management can lead to prolonged recovery, chronic pain, or even complications. Here’s a detailed guide to ensure optimal recovery and prevent further damage.
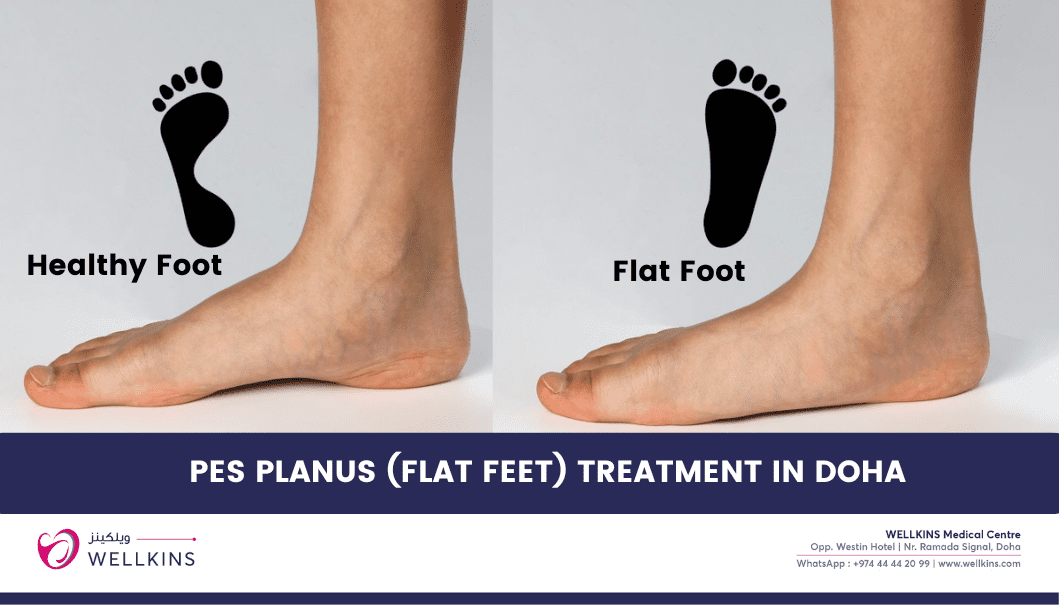
Flat feet is when one or both feet have no arches or arches that are very low. This can cause feet to lie fully flat on the ground, which can impair a person’s posture. Flat feet may also cause pain and discomfort.
What Are Flat Feet?
Flat feet occur when the arches of the feet collapse, causing the entire sole to come into contact with the ground. This condition can be present from childhood (congenital) or develop over time due to factors like aging, injury, or obesity.
When to Investigate Flat Feet
Not all cases of flat feet require medical intervention. However, investigations are warranted if:
Pain is present:
Pain in the feet, ankles, knees, hips, or lower back may indicate strain caused by flat feet.
Swelling or stiffness:
Persistent swelling or stiffness along the inner side of the foot may suggest tendon dysfunction (e.g., posterior tibial tendon insufficiency).
Changes in foot shape:
A noticeable flattening of the arch over time or a foot that appears to be rolling inward (overpronation) should be evaluated.
Difficulty walking or standing:
If flat feet are affecting mobility or causing fatigue, further assessment is needed.
Associated conditions:
Patients with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, or obesity may require closer monitoring.
Investigations for Flat Feet
To diagnose and assess the severity of flat feet, the following investigations may be performed:
1.Physical Examination:
Observation of the foot’s shape while standing and walking.
Checking for tenderness, swelling, or limited range of motion.
Assessing gait and alignment of the lower limbs.
2.Imaging Studies:
X-rays:
To evaluate the bony structure and alignment of the feet.
MRI:
To assess soft tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, especially if posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is suspected.
CT Scan:
For detailed evaluation of complex deformities or surgical planning.
3.Foot Pressure Analysis:
Gait analysis or pressure mapping to assess weight distribution and identify areas of excessive stress.
4.Common Laboratory Tests for Flat Feet
Metabolic and Endocrine Tests–
Calcium, Phosphorus, and Alkaline Phosphatase: Assess bone metabolism, Abnormal levels may indicate metabolic bone diseases (e.g., osteoporosis or rickets) that can affect foot structure.
Vitamin and Mineral Levels–
Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals can affect bone and tendon health.
Vitamin D Levels:
Low levels can lead to bone softening (osteomalacia) and contribute to flat feet.
Serum Calcium and Magnesium:
Essential for bone health and muscle function.

When to Worry About Flat Feet;
Flat feet are usually not a cause for concern, but you should seek medical attention if:
Pain or discomfort interferes with daily activities.
Symptoms worsen over time.
There is a sudden collapse of the arch (may indicate posterior tibial tendon dysfunction).
You notice asymmetry (one foot is flatter than the other).
There are signs of nerve compression or circulation issues (numbness, tingling, or cold feet).
Treatment Options for Flat Feet
The treatment approach depends on the severity of symptoms and the underlying cause. Here are the options:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
Footwear Modifications: Supportive shoes with good arch support and cushioning can alleviate symptoms. Custom orthotics may be recommended for added support.
Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises for the Achilles tendon, calf muscles, and foot arches can improve stability and reduce pain.
Weight Management: Losing weight can reduce stress on the feet and improve symptoms.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen) or anti-inflammatory medications can help manage discomfort.
Bracing: In some cases, a brace or ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) may be used to support the foot and correct alignment.
2. Surgical Treatments
Surgery is considered only when conservative measures fail and symptoms are severe. Surgical options include:
Tendon Repair or Transfer: To correct posterior tibial tendon dysfunction.
Osteotomy: Cutting and realigning bones to restore the arch.
Arthrodesis: Fusing joints to stabilize the foot.
Implants: Inserting devices to support the arch.
Prevention and Long-Term Care for flat feet
Wear supportive footwear, especially during physical activities.
Avoid high-impact activities that strain the feet.
Perform regular foot exercises to maintain strength and flexibility.
Monitor for any changes in foot shape or function, especially if you have risk factors like diabetes or arthritis.
Conclusion
Flat feet are a common condition that rarely requires intervention unless they cause pain or functional limitations. If you’re experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult an orthopedic specialist. With proper evaluation and treatment, most patients can achieve significant relief and maintain an active lifestyle. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing complications. If you have concerns about flat feet, schedule an appointment with your orthopedic surgeon for a thorough assessment.
Read more about the orthopedic services at wellkins here: https://wellkins.com/orthopedics/