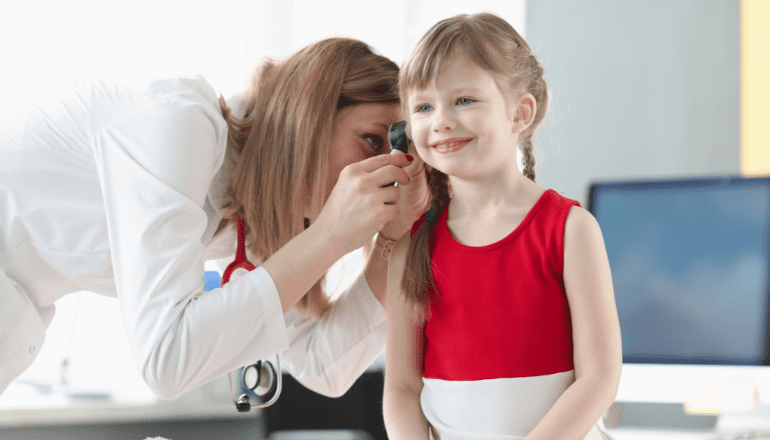
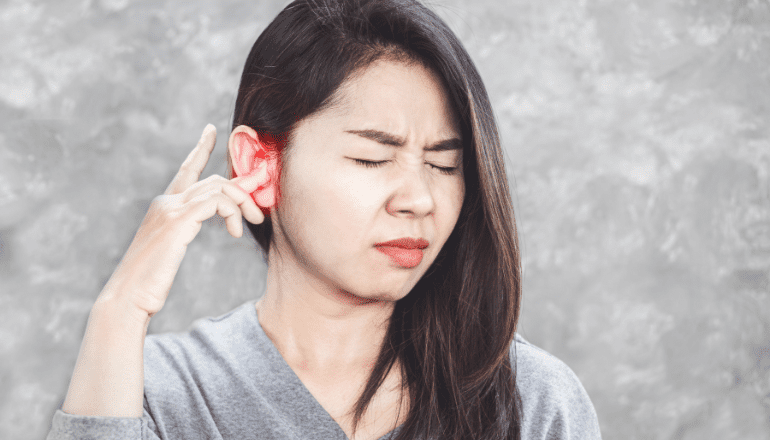
Author: Dr.Preethi Sarma (ENT Specialist – WELLKINS Medical Centre)
Ear infections are common health issues that affect both children and adults. They usually occur when the middle ear (the part of the ear behind the eardrum), becomes inflamed or infected. We will now discuss how to identify and treat middle-ear infections in both age groups.
Symptoms of Ear Infections include:
- Ear Pain: Especially in children, ear pain is a common and prominent symptom. Adults may also experience ear pain.
- Hearing Loss: Temporary hearing impairment, ranging from mild to moderate, can occur.
- Ear Fullness: A feeling of fullness or pressure in the affected ear.
- Tinnitus: Ringing, buzzing, or other noises in the ear that are not related to external sounds.
- Ear Discharge: In some cases, fluid or pus may drain from the ear, indicating a perforated eardrum.
- Fever: Especially in children, an ear infection can be accompanied by a fever.
- Irritability: In infants and young children, increased fussiness and irritability can be a sign of ear pain.
- Sleep Disturbances: Children may have trouble sleeping due to the discomfort.
- Balance Issues: Inner ear involvement can lead to dizziness or problems with balance.
- Difficulty in Young Children: Infants and toddlers may tug at their ears or have changes in appetite and behavior due to ear discomfort.
It’s important to note that not all of these symptoms may be present, and the severity can vary from person to person. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of an ear infection, it’s advisable to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Ear infections are prevalent health concerns that impact individuals of all ages. Ear infections can cause discomfort and hearing impairment, but with timely identification and appropriate treatment, they can be managed effectively.
Identifying Ear Infections
Ear infections can result from various factors, including bacterial and viral sources. Notably, the anatomy of infants and children plays a role in their higher susceptibility to these infections. In this age group, the Eustachian tube, which links the middle ear cavity to the upper throat (nasopharynx), is shorter, wider, and more horizontally oriented. This unique anatomy can facilitate the entry of fluids from the throat into the middle ear, increasing the likelihood of infections.
Furthermore, infants fed in a horizontal position may inadvertently introduce fluids into the Eustachian tube, potentially leading to middle ear infections. Another critical point to consider is the presence of perforations in the ear drum, as they provide a pathway for infection to reach the middle ear.
It’s imperative to recognize the warning signs of a severe infection that has spread beyond the ear. Symptoms such as dizziness, severe headache, nausea, high fever, seizures, neck or ear swellings, irritability, vision problems, or facial weakness should not be taken lightly. These manifestations indicate a potential spread of infection beyond the ear, requiring immediate medical attention to address the broader health implications.
Treatment of Ear Infections
The treatment for an ear infection can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection.Treatment options include antibiotics, pain relievers, decongestants, antihistamines, ear drops, ear toilet etc. The treatment option varies if any red flags develop during the course of the illness. All cases should have a careful follow-up until the ear drum returns to its normal appearance and deafness disappears.
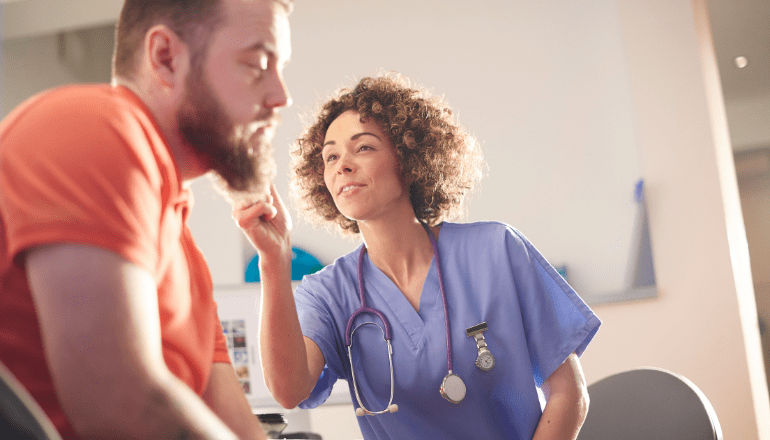

Preventing Ear Infections: A Guide for All Ages
Protecting your ears from infections is crucial for overall well-being. Here are key steps to prevent ear infections in both children and adults:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly wash your hands to prevent the spread of germs. Avoid self-cleaning of the ears, as it can push wax deeper and increase infection risk.
- Say No to Smoking: Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, which can irritate the ears and heighten infection vulnerability.
- Vaccination: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations, especially for illnesses like the flu and pneumococcus, known to contribute to ear infections.
- Protect from Loud Noises: When exposed to noisy environments, wear ear protectors like earplugs or earmuffs, especially in loud workplaces.
- Early Treatment for Allergies and Respiratory Infections: Promptly address allergies and respiratory infections, as these conditions elevate the risk of ear infections
Ear infections can cause discomfort and pain, but with proper treatment and prevention strategies, they can be effectively treated and prevented. If you or your child is experiencing symptoms of an ear infection, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the best course of treatment. By following these guidelines, you can help protect your ears and prevent future ear infections. Remember, prevention is key to maintaining good ear health!